Overview: Rapid technology evolution in recent decades is leading to increasingly complex systems that integrate multiple functions to meet various technological demands. Efficient system reliability assessment techniques need to be developed for such complicated systems with multiple components and multiple failure mechanisms, in order to ensure adequate performance under uncertain and extreme demands.
This research develops a new system reliability assessment method by expanding the basic Petri net methodology. Petri nets are adapted to simulate the failure mechanisms and dynamic processing of systems. The interactions in components are shown by arcs. The different states of the system are shown as different markings. The uncertainty associated firing delay of transitions is computed by propagating input uncertainties through the system analysis model. In addition, a Bayes net is constructed as a sub net of the Petri net-based system model to facilitate updating of various uncertainties based on inspection data. Inspection, maintenance and repair are easily implemented by adding several places, transitions and arcs to the model. Different preventive maintenance schedules can be added by defining of different thresholds for no maintenance, minor maintenance, major maintenance and repair.
The contributions of the proposed methodology are (1) it can effectively simulate the failure mechanism and dynamic process of systems in a straightforward and multi-state fashion; (2) it can incorporate preventive maintenance in the system reliability assessment; and (3) it can reduce subjectivity in the context of preventive maintenance schedule by providing quantitative information.
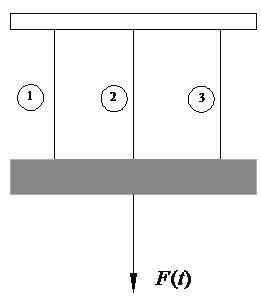
Example Applications: The proposed methodology is illustrated with a three bar parallel system subject to fatigue loading.
 |
 |
 |
|
(a) Three bar parallel system
|
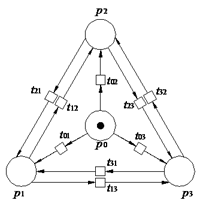
(b) Petri net model without repair
|
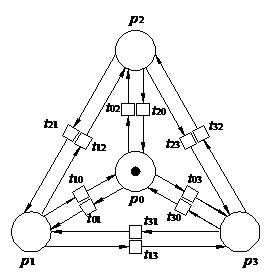
(c) Petri net model with repair
|
Potential Applications: Petri net is mostly used in computer science and automatic control since its origination in 1962 to get the performance estimation of those systems. In this research its application is extended to performance and reliability analysis of degraded structures. So the proposed reliability analysis methodology and preventive maintenance strategy can be applied to both structural and mechanical systems.